Abstract
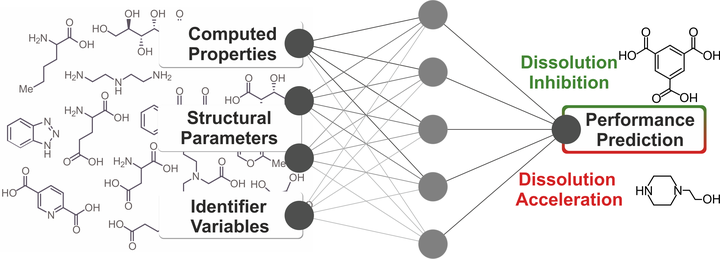
The vast number of small molecules with potentially useful dissolution modulating properties (inhibitors or accelerators) renders currently used experimental discovery methods time- and resource-consuming. Fortunately, emerging computer-assisted methods can explore large areas of chemical space with less effort. Here we show how density functional theory calculations and machine learning methods can work synergistically to generate robust and predictive models that recapitulate experimentally-derived corrosion inhibition efficiencies of small organic compounds for pure magnesium. We further validate our methods by predicting a priori the corrosion modulation properties of seven hitherto untested small molecules and confirm the prediction in subsequent experiments.